Blog
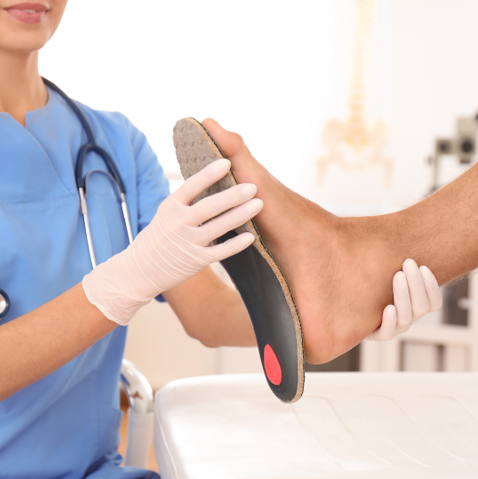
December 4, 2025
December is the season of giving, and there’s no better gift than comfort. If you’re looking for something meaningful, helpful, and long-lasting, custom orthotics are a great choice. They support the feet, improve balance, and make everyday activities easier and more comfortable. Why Orthotics Make a Great Gift Many people struggle with foot pain, tired feet, or discomfort when walking or standing. Custom orthotics can help by: Reducing foot, heel, and arch pain Providing better alignment and support Improving comfort during work, exercise, and daily routines Helping prevent future foot problems They are a thoughtful gift for anyone—especially those who stay on their feet all day, enjoy being active, or dealing with ongoing foot issues. How Our Team Can Help Our podiatry team offers: Custom Orthotic Fittings tailored to your foot shape and needs Foot Evaluations to identify pain points and pressure areas Supportive Shoe Recommendations for everyday comfort Ongoing Care for long-term foot health Give Comfort This Christmas If you’re searching for a gift that truly helps someone feel better, custom orthotics are a smart and meaningful choice. Contact our office to schedule an appointment or learn more about how orthotics can bring comfort all year long.

November 7, 2025
November marks National Diabetes Awareness Month , a time dedicated to raising awareness, supporting those affected, and sharing ways to live healthier with diabetes. With diabetes impacting millions of Americans, proactive foot care remains one of the most important—and often overlooked—parts of diabetes management. Why Foot Health Matters Diabetes can affect the feet in several ways, and early prevention is key. High blood sugar levels may lead to: Nerve damage (neuropathy) that causes numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation Reduced blood flow , slowing the healing process Higher risk of infections, wounds, and ulcers , which can become serious if left untreated Healthy, routine foot care can help prevent complications and support mobility, comfort, and long-term wellness. How Our Podiatry Team Supports Diabetic Foot Health We provide comprehensive diabetic foot care to protect, prevent, and treat foot-related concerns, including: Routine Diabetic Foot Exams Early detection and intervention to address concerns before they become more serious. Custom Orthotics Personalized support to improve balance, relieve pressure points, and enhance walking comfort. Advanced Wound Care Specialized treatment plans for wounds, ulcers, or injuries to promote faster healing and reduce risks. Footwear Guidance Recommendations for proper shoes and inserts designed to prevent irritation, friction, and injury. We’re Here to Help You Stay Healthy Caring for your feet is an essential part of staying active, independent, and healthy with diabetes. Whether you have questions about preventive care, footwear, or treatment options, our podiatrists are here to guide and support you every step of the way. This month is a great time to schedule a diabetic foot check or talk with us about ways to keep your feet protected year-round. Together, we can work toward better foot health and a healthier life with diabetes.

September 9, 2025
As temperatures drop and race season picks up, fall is the perfect time to refresh your running gear and hit the pavement, trails, or treadmill with confidence. Whether you’re training for your first 5K, prepping for a marathon, or simply enjoying crisp outdoor walks, choosing the right running shoe is essential to protecting your feet and keeping you moving injury-free. Our podiatrists—experts in both foot health and running biomechanics—have shared their top shoe recommendations to suit a wide range of runners, foot types, and fall activities. �55356;�57283;♀️ Best for Everyday Training & Long Distances Hoka Clifton 10 This lightweight, max-cushioned shoe is a favorite among neutral runners. It’s a reliable “workhorse” option for everyday runs or long distances, with plush support and breathable materials. Heel and midfoot strikers will appreciate the comfort, while the soft interior cushions repetitive impact—ideal for runners logging serious miles. �55358;�56781;♂️ Best for Stability & Support Puma ForeverRun Nitro 2 Need more structure? This stability shoe offers broad midfoot support and a snug heel for added control, making it a great choice for overpronators or those seeking extra reinforcement on long runs. A springy midsole absorbs shock and protects joints on hard surfaces like concrete and asphalt. ASICS Gel-Kayano 32 Another top-tier pick for stability, the Kayano provides plush cushioning and firm arch support. It’s a go-to option for marathoners or anyone prone to overpronation looking for long-lasting comfort on high-mileage days. Brooks Adrenaline GTS Flat-footed runners love this shoe for its supportive structure and reliable cushioning. It’s an excellent balance of motion control and responsiveness, keeping your gait aligned and reducing injury risk over time. �55357;�56415; Best for Beginners or Versatile Runners Brooks Ghost 17 A crowd favorite for its balanced cushioning, smooth transitions, and lightweight feel. This versatile shoe is perfect for newer runners or those unsure of their foot strike pattern. With updates that benefit both forefoot and heel strikers, it’s a safe bet for most training needs. ASICS Gel-Nimbus & Saucony Triumph These shoes are excellent options for runners with high arches who need a bit more cushioning and comfort for impact protection. �55356;�57138; Best for Trail Running Altra Olympus 6 For runners who prefer rugged terrain and natural surfaces, the Olympus 6 provides ample protection from rocks, roots, and uneven trails—without sacrificing comfort. It’s well-padded to prevent foot fatigue and boasts a roomy toe box, making it ideal for wide-footed runners or those who prefer a zero-drop design for a more grounded feel. �55356;�57119; Honorable Mentions by Foot Type For Flat Feet: Brooks Adrenaline GTS, ASICS Gel Kayano 32, Hoka Gaviota, Saucony Guide For High Arches: Brooks Ghost, ASICS Gel Nimbus, Saucony Triumph For Plantar Fasciitis: Brooks Adrenaline, ASICS Kayano, Hoka Clifton or Bondi For Wide Feet/Minimalist Preference: Altra Torin — known for a zero-drop platform and wide toe box �55356;�57281; Final Tips for Race Season Whether you're training for a fall race or upping your fitness game, remember: the right shoe can make all the difference in performance and injury prevention. If you’re experiencing discomfort, blisters, heel pain, or foot fatigue, it may be time for a professional shoe assessment—or a podiatric consultation. Our podiatry team is here to help you put your best foot forward this fall. Schedule an appointment to get fitted for the perfect pair and make sure your feet are race-day ready!

August 22, 2025
As the school year kicks off, most parents are focused on school supplies, lunchboxes, and new routines—but one of the most important back-to-school essentials is often overlooked: a good pair of shoes. Children and teens spend hours on their feet every day—walking through school hallways, running during recess, or playing sports after school. The right footwear doesn’t just offer comfort; it plays a vital role in supporting growing feet, preventing injuries, and setting kids up for a healthy, confident school year.

May 1, 2025
As temperatures rise and flip-flops come out in full force, it’s important not to overlook your feet when it comes to summer care. Whether you're heading to the beach, walking around amusement parks, or just enjoying backyard barbecues, your feet need protection and support to keep you moving comfortably all season long.

By info
•
April 10, 2025
Your feet are the foundation of your body, supporting you with every step you take. We understand that maintaining foot health is crucial to your overall well-being and mobility. In honor of April being National Foot Health Awareness Month, this blog explores why foot health should never be overlooked and provides tips for keeping your feet healthy. Why Foot Health Matters The human foot is a complex structure of 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This intricate design allows for movements such as walking, running, and jumping. However, it also means that many things can go wrong if not cared for properly. Poor foot health can lead to a range of issues from simple aches and pains to more severe conditions like plantar fasciitis or diabetic neuropathy. Moreover, problems in your feet can affect other parts of your body, including your knees, hips, and back. Tips for Maintaining Healthy Feet Regular Check-ups: Just like regular dentist visits, regular check-ups with a podiatrist, especially during National Foot Health Awareness Month, can help catch foot problems before they become serious. Proper Footwear: Wear shoes that fit well and provide good support. Different activities require different types of shoes – what you wear for running is not suitable for a day at work. Foot Hygiene: Wash your feet daily, dry them thoroughly to prevent infections, and change socks daily. Stay Active: Regular exercise helps keep your feet and body healthy. Remember to stretch your feet and ankles before and after workouts. Manage Your Weight: Extra weight puts additional pressure on your feet, increasing the risk of foot disorders. Common Foot Conditions and Treatments Plantar Fasciitis: Often felt as heel pain, treated with exercises, proper footwear, and sometimes orthotics. Bunions: Misaligned big toe joints that can become swollen and tender. Treatment options include wearing comfortable shoes, pads, and in severe cases, surgery. Diabetic Foot Care: People with diabetes need to take extra care of their feet as poor blood circulation and nerve damage can lead to serious foot problems. We believe in a proactive approach to foot health. Whether you're an athlete, a busy professional, or enjoying retirement, taking good care of your feet is a step toward a healthier life. Celebrate National Foot Health Awareness Month with us and schedule an appointment today to learn how you can better care for your feet and enhance your overall wellness.

March 1, 2025
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty walking. They occur when the joint at the base of the big toe becomes misaligned, leading to a bony bump on the side of the foot. While bunions can develop due to genetics, improper footwear, or other factors, the good news is that advancements in podiatric care have made treatment and prevention more effective than ever. If you’re struggling with a bunion, seeing a podiatrist can provide relief and help you regain your mobility.



